Author: Shihao Fu, Technology Analyst at IDTechEx
The autonomous truck industry is experiencing a significant revival, with vehicle delivery numbers continuously breaking records. Companies across Asia, Europe, and the United States are eagerly advancing into the commercialization testing phase. Autonomous trucks are addressing critical real-world issues by reducing transportation costs and optimizing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) through meticulous, practical calculations.
In the report, “Autonomous Trucks 2024-2044: Technologies, Trends, Forecasts“, IDTechEx conducts a comprehensive TCO analysis across different levels of autonomy and powertrain types, focusing on the cost structures in the United States and China. This analysis considers the disparities in procurement costs, maintenance, and operational expenses between the two markets.
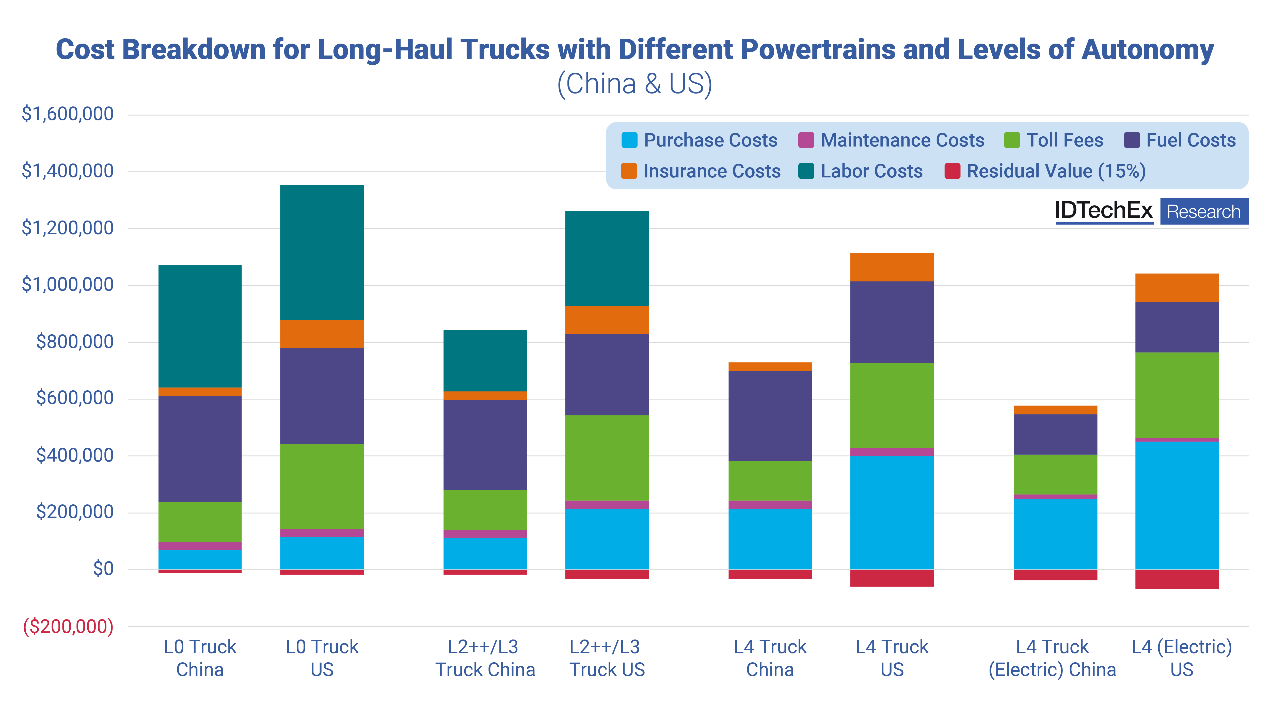
Cost breakdown for long haul trucks with different powertrains and levels of autonomy. Source: IDTechEx
A decade of operational insights
IDTechEx’s analysis applies these cost factors to a 10-year operational model, utilizing exclusive data obtained from their research targets. Compared to other TCO analyses in the industry, IDTechEx have refined the evaluation of maintenance and operational costs in various markets, considering factors such as depreciation, highway tolls, management fees, and insurance.
Key differences in operational costs between China and the US
Through a detailed TCO analysis of different types of autonomous trucks in both China and the US, IDTechEx identified several critical factors driving cost differences, including purchase prices, maintenance expenses, fuel costs, and unique market conditions.
- Purchase costs: For mid-to-high-end Level 0 (non-autonomous) trucks, the purchase cost in China is approximately US$70,000, compared to US$114,286 in the US, representing a 63% difference. This disparity stems from significant differences in manufacturing costs, market scale, and labor expenses between the two countries. China's robust manufacturing infrastructure and large-scale production capabilities enable lower truck production costs. Additionally, the large demand for trucks in China further reduces the cost per vehicle through economies of scale.
- Advanced autonomous vehicles: For Level 2/Level 3 autonomous trucks, the reference purchase cost in China is US$112,000, while in the US, it is US$214,286—about 91% higher. The cost of developing and integrating autonomous systems is relatively higher in the US, coupled with stringent regulations that demand higher technical maturity and safety standards, driving up the cost of these advanced models. The cost gap is even more pronounced when analyzing Level 4 autonomous electric trucks, with reference purchase costs of US$250,000 in China versus US$450,000 in the US.
- Electric platform considerations: The upfront cost of electric trucks at Level 4 Autonomy, is largely determined by the required battery pack size. Lithium-ion battery packs are priced between US$160 and US$200 per kWh, with a typical 150 kWh battery for a medium-duty truck costing over US$25,000, while a heavy-duty truck with a 400 kWh battery could see costs exceeding US$65,000. In recent years, China’s booming electric vehicle market has significantly optimized battery material costs and supply chains. Coupled with government subsidies and economies of scale, China’s advantage in electric vehicle production is difficult to challenge purely through market forces. The Chinese government’s robust support for electric vehicles, including the construction of charging infrastructure and purchase subsidies, has substantially reduced the cost of acquiring electric trucks. Conversely, in the US, while the electric vehicle market is growing rapidly, there is relatively less infrastructure and policy support, leading to higher purchase and operating costs. IDTechEx believes this cost differential will be evident in the early stages of market adoption for autonomous electric trucks, as seen in China’s consumer electric vehicle market.
Fuel and energy cost comparison
Fuel costs are another crucial factor influencing TCO. For Level 0 trucks, fuel costs in China are calculated at US$371,429, compared to US$336,576 in the US. This difference primarily reflects the variation in fuel prices between the two countries. While fuel prices are lower in China, higher fuel taxes—often accounting for up to 48%—result in relatively higher actual usage costs. In contrast, fuel prices in the US are more volatile but are accompanied by standardized fuel taxes, resulting in overall lower fuel costs.
For Level 4 electric trucks, the energy cost difference is even more pronounced, with energy costs in China at US$141,780 versus US$177,480 in the US. This disparity not only reflects significant differences in electricity prices but also relates to the prevalence of charging infrastructure, charging speed, and the cost structure of power generation.
The impact and adaptability of electric powertrains on TCO
Compared to traditional internal combustion engines, electric trucks will increasingly demonstrate cost advantages in long-term operations. Firstly, energy costs for electric trucks are relatively stable, and as global efforts to promote green energy continue, future electricity costs could decrease further. IDTechEx’s battery price forecasts suggest that by 2030, the average price for batteries and battery packs will reach approximately US$100 per kilowatt-hour. Reducing the cost of truck battery packs will be key to the widespread deployment of battery electric vehicle (BEV) trucks.
Moreover, electric trucks have lower maintenance costs than traditional trucks due to the high reliability of electric motors and battery systems, with fewer components requiring regular maintenance. However, the TCO advantage of electric trucks extends beyond direct costs. Electric trucks can reduce carbon emissions, which could lead to additional policy incentives or carbon tax reductions, further lowering their total cost of ownership. As battery technology continues to advance, improvements in battery life and energy density, along with shorter charging times, will enhance the economic viability and market competitiveness of electric trucks.
Given China's leading position in the electric vehicle market and strong government support, the country is likely to maintain lower acquisition costs for electric trucks in the short to mid-term, further promoting their adoption in the Chinese market.
The IDTechEx report, “Autonomous Trucks 2024-2044: Technologies, Trends, Forecasts”, provides a comparative analysis of TCO in China and the US across different levels of autonomy and powertrain types. It also delves into the market factors driving these cost differences. IDTechEx’s analysis offers valuable insights for industry participants, helping them make more informed decisions in the global market.
To learn more about this new IDTechEx report, including downloadable sample pages, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/AutoTrucks.
For the full portfolio of autonomy market research available from IDTechEx, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/Research/Autonomy.




